East Africa Time
East Africa Time is a topic that has sparked interest and debate over the years. Since its inception, it has captured the attention of people of all ages and interests, becoming a cultural phenomenon that transcends borders and generations. In this article, we will explore different perspectives and approaches related to East Africa Time, from its impact on society to its relevance today. Through a detailed analysis, we seek to better understand this phenomenon and its influence in various areas, thus allowing a broader and enriching understanding of East Africa Time.
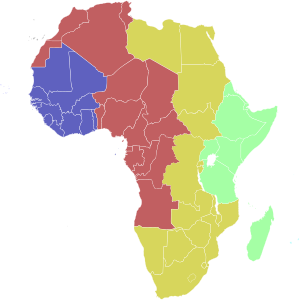
Time zones of Africa:
a The islands of Cape Verde and Canary Islands are to the west of the African mainland.
b Mauritius and the Seychelles are to the east and north-east of Madagascar respectively.
This article needs additional citations for verification. (December 2009) |

| Light Blue | Cape Verde Time (UTC−1) |
| Blue | Greenwich Mean Time (UTC) |
| Red | (UTC+1) |
| Ochre | (UTC+2) |
| Green | East Africa Time (UTC+3) |
| Turquoise | (UTC+4) |
b Mauritius and the Seychelles are to the east and north-east of Madagascar respectively.
East Africa Time, or EAT, is a time zone used in eastern Africa. The time zone is three hours ahead of UTC (UTC+03:00), which is the same as Moscow Time, Arabia Standard Time, Further-eastern European Time and Eastern European Summer Time.[1]
As this time zone is predominantly in the equatorial region, there is no significant change in day length throughout the year and so daylight saving time is not observed.[1]
East Africa Time is observed by the following countries:[2]
See also
- Moscow Time, an equivalent time zone covering Belarus, Turkey and most of European Russia, also at UTC+03:00
- Arabia Standard Time, an equivalent time zone covering Bahrain, Iraq, Kuwait, Qatar, Saudi Arabia and Yemen, also at UTC+03:00
- Eastern European Summer Time, an equivalent time zone covering European and Middle Eastern countries during daylight saving, also at UTC+03:00
- Israel Summer Time, an equivalent time zone covering the State of Israel during daylight saving, also at UTC+03:00
- Further-eastern European Time, an equivalent time zone covering extended Eastern European countries, also at UTC+03:00
References
- ^ a b "EAT Time". World Time Zones.Org. Archived from the original on 10 February 2011. Retrieved 29 April 2012.
- ^ "Eastern Africa Time – EAT Time Zone". www.timeanddate.com. Retrieved 2023-09-26.